An average gross profit margin is around 10%, with over 20% considered good. For example, if ABC Services has a gross profit margin of 63.26% for the month of May, it means the company was able to convert more than 63% of its revenue into profit. The gross profit ratio only shows the profitability of a business, not its liquidity or cash position. Also, it doesn’t consider other expenses that are necessary for running the company’s operations. Shifting consumer tastes and preferences can force companies to adjust their product offerings.
- Nonetheless, the gross profit margin should be relatively stable except when there is significant change to the company’s business model.
- Profit margin is the percentage of profit that a company retains after deducting costs from sales revenue.
- While the gross profit margin measures the profitability of a production process, net profit margin considers all of the expenses a company takes on—not just the ones linked to production.
- Conversely, a decrease in demand might necessitate discounts or promotions, which can depress the margin.
Net Profit to Gross Profit Ratio

The best way to assess a company’s gross margin number is to conduct a long-term analysis of trends, comparing the company to itself, or to compare it to peers and the sector average. Based on PG’s most recent quarterly gross profit of 47.38%, it has an excellent gross profit relative to its sector. The best way to interpret a company’s gross margin is to analyze the trends over time and compare the number to the industry and peers. Companies can use gross margin as a guideline to improve their operations and adjust pricing strategies. While the gross margin only accounts for a company’s COGS, the net margin accounts for COGS plus all indirect, interest, and tax expenses.
- A company might strive to slash labor costs or source cheaper suppliers of materials if its gross margin is falling or it may decide to increase prices as a revenue-increasing measure.
- However, this can result in a decline in quality, so you need to be careful about monitoring the quality of incoming components.
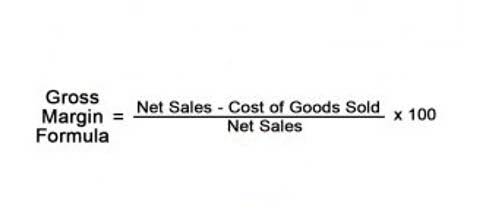
- The Gross Margin is a profitability ratio that measures the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS) incurred in the period.
- Pay attention to the price, and buy in bulk when prices are low or supplies are on sale.
- This metric is usually expressed as a percentage of sales, also known as the gross margin ratio.
- If a company’s home currency strengthens considerably against other currencies, its products might become more expensive for foreign customers, potentially impacting sales and margins.
The Difference Between Gross Margin and Gross Profit
For businesses operating internationally, currency exchange rate volatility can be a significant challenge. If a company’s home currency strengthens considerably against other currencies, its products might become more expensive for foreign customers, potentially impacting sales and margins. gross margin accounting The first step is determining your total revenue or net sales, which entails adding up all the income generated from selling goods or services during a specific period. In highly competitive markets, companies might be compelled to reduce prices, which can erode the gross margin.
What Is a Good Gross Profit Margin?
Gross margin differs from other metrics like net profit margin because it exclusively considers the costs directly tied to production. If you offer multiple goods or services, you may discover they don’t all perform equally well. Even products that sell a large volume may not be very profitable if they demand a large amount of materials and labor costs. Assess which products deliver the best profit and consider whether you could cut poorly performing products and focus on more profitable ones.

Impact on profit

Furthermore, securing venture capital and other venture fund sources can become challenging during these times since investors may become more conservative with where they place their money. As such, this can affect your profit margin, making it even more essential for businesses to optimize operations. On the other hand, gross margin is expressed as a percentage and represents the proportion of gross profit relative to net sales revenue. It provides a more standardized measure of profitability, allowing for easy comparison between companies of different sizes or industries. Gross profit is the monetary value after subtracting the COGS from net sales revenue.
This obviously has to be done competitively otherwise goods will be too expensive and customers will shop elsewhere. The above result means that for every dollar Joe’s Auto Shop brings in, 49.16% of it is available to pay for operations. You can also dive deeper, analyzing how PG compares to its top competitors. Two such companies are Colgate-Palmolive (CL) and the Kimberly-Clark Corporation (KMB). Both views provide insights into different aspects of the company’s operations. They can pay dividends to shareholders, reinvest in the business, buy back their shares, or reduce their debt.
- The Ascent is a Motley Fool service that rates and reviews essential products for your everyday money matters.
- It measures the ability of a company to generate revenue from the costs involved in production.
- Improving gross margin can be done by increasing sales price, reducing costs of goods sold, and improving product or service design.
- A profit margin of 20% indicates a company is profitable, while a margin of 10% is said to be average.
- Since this ratio measures the profits from selling inventory, it also measures the percentage of sales that can be used to help fund other parts of the business.
- When a company has a higher profit margin, it means that it operates efficiently.